The Accounting Process
The Accounting Process begins with the analysis of transactions. Then accountants record the transactions in journal, then post to ledger, prepare trial balance, adjust for matching principles, and finally prepare income statement and balance sheet. In this section, we start with analyzing transactions in accounting equation, then give example of journal, ledger, and finally prepare unadjusted trial balance.
In this section:
- What is accounting process?
- How we get Accounting Equation.
- Analyzing transactions and their impact on accounting equation.
- Preparing journal entries
- Posting to ledger accounts
- Preparing trial balance
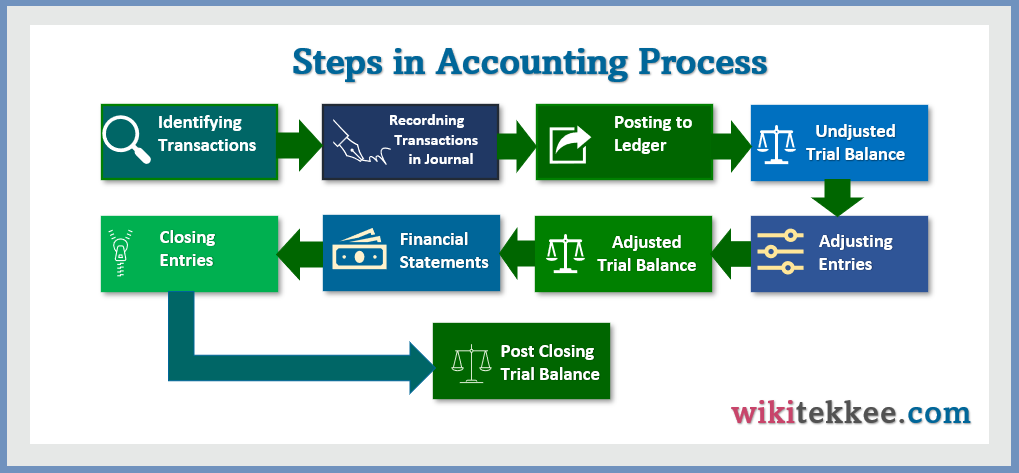
1. What is Accounting Process:
The Accounting process involves a series of steps followed by business entities. The steps are identifying economic transactions, classifying them, recording them in journals, posting to ledgers, preparing trial balance, preparing adjusting entries and adjusted trial balance, preparing income statement, and finally preparing the post-closing trial balance. Currently, three main financial statements are prepared from adjusted trial balance, namely Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement, and Balance Sheet. Some accountant also prepare four different statements, and the fourth one is statement of owners’ equity.
Steps in the Accounting process:
1. Identifying the Transactions:
The first step in the accounting process is the identification of business transactions. While identifying transactions, accountants have to be careful enough to identify only those transactions that are financial in nature and affect company’s money. Accounting can record only financial transactions, not any event that does not affect finance of the company. For example, the death of CEO is not a financial transaction even though this event affect the company’s stock price.
2.Recording Transactions in the Journal:
The second step in the accounting process is the recording of financial transactions in journal. How the transactions will be recorded depends on the accounting basis followed by company. The company may follow either accrual basis or cash basis of accounting. In Cash basis of Accounting, accountant records only those transactions that directly affect cash–either paid in cash or received in cash. On the other hand, under the accrual basis of accounting, revenues or expenses are recorded in the period when they are earned or incurred. In double entry accounting system, every single transaction affects two accounts–one of them are debited and the one is credited. For example, sales in cash affects two accounts–Cash and Sales revenue.
3.Posting Transactions from Journals to Ledgers:
After completing the journal entries, every account is then posted to its respective ledger account. The ledger account balance helps users to know the debit or credit balance of each account. If an account is debited in journal entry, that account is posted to the debit side of ledger account. For example, we have a journal entry:
Cash—————–Dr. 1,000
Sales revenue————Cr. 1,000
When we post this journal to ledger, the cash account will be posted on the debit side of CASH account, indicating that by this transaction cash balance has increased by $1,000.
4. Preparation of Unadjusted Trial Balance:
After the preparation of ledger accounts, all the balances from ledger accounts are listed in a tabular format, which is called trial balance. A trial balance is the list of all the accounts from ledger. The main purpose of trial balance is to check whether there is any error in the journal and ledger. If there is any error in the journal or ledger, the trial balance will not be balanced. By seeing the trial balance users can know the balances of individual accounts at a glance.
5. Preparing Adjusting Entries:
After the preparation of unadjusted trial balance, accountants need to prepare adjusting entries to make sure that they follow the matching principle of accounting. Some transactions are not complete until the end of the accounting period. For example, prepaid insurance is adjusted at the end of every accounting period.
6. Preparing Adjusted Trial Balance:
After the preparation of adjusting entries, the final trial balance, Adjusted Trial Balance, is prepared. This trial balance is the list of all accounts after making all the necessary adjustments. Then the financial Statements are prepared from this trial balance.
7. Preparation of Financial Statements:
Once the adjusted trial balance is prepared, the accountants are now ready to prepare the financial statements–Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement, and Balance Sheet. To know the net income or loss, the income statement is prepared, to know the company’s cash position, the cash flow statement is prepared, and finally to know the position of assets and liabilities of companies, the balance sheet is prepared.
8. Preparing Closing Entries:
The main purpose of closing entry is to transfer the balances of temporary accounts to permanent accounts. For example, the expenses accounts are closed to income statement, and the balance of income statement is closed to owners’ equity account. The temporary accounts are revenues, expenses, and the balance of income statement. Permanent accounts are assets, liabilities, and retained earnings.
9. Preparing Post-closing Trial Balance:
After the preparation of closing entries, the final trial balance, the post closing trial balance, is prepared. The post-closing trial balance is actually the list of all the permanent accounts. From this trial balance, users can see the net balances of assets, liabilities, and retained earnings.
2. How do we get the Accounting Equation:
We know the Accounting Equation is Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity. There is a common question, “how do we get this accounting equation?” Let’s discuss the accounting equation. Let’s take an example. We want to start a business, and to start the business, we need 10 million dollar. We, the owners, have only 8 million dollar, and we borrowed the remaining 2 million dollar from outsiders. We are the owners of the business, and the outsiders, who provided the 2 million dollar, are the liabilities of the business. The total amount of money, $10M, the business owns is assets. Therefore, in the business, we have:
- Total Assets of $10M.
- The first part of $2M goes to the outsiders, the Liabilities.
- The remaining part of the business assets, $8M, goes to the owners.
Now, we can say write the equation as $10M=$2M+$8M, which is actually Assets = Liabilities + Owners’ Equity.
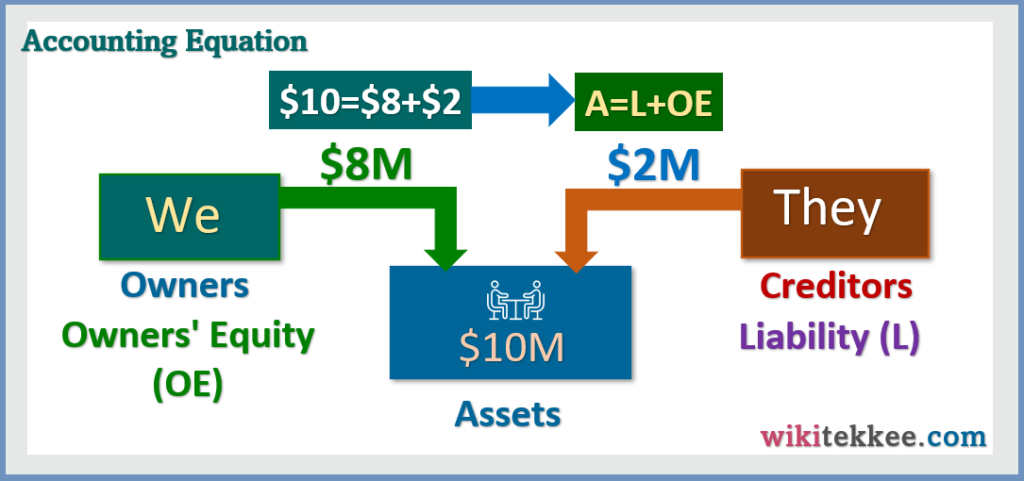
This is how we get the Accounting Equation A= L+ OE.
3. Analyzing Transactions and their impacts on Accounting Equation:
Before analyzing transactions and their impact on accounting equation, accountants have to identify the type of accounts involved, and then determine whether the accounts are affected positively or negatively. Let’s analyze some transactions.
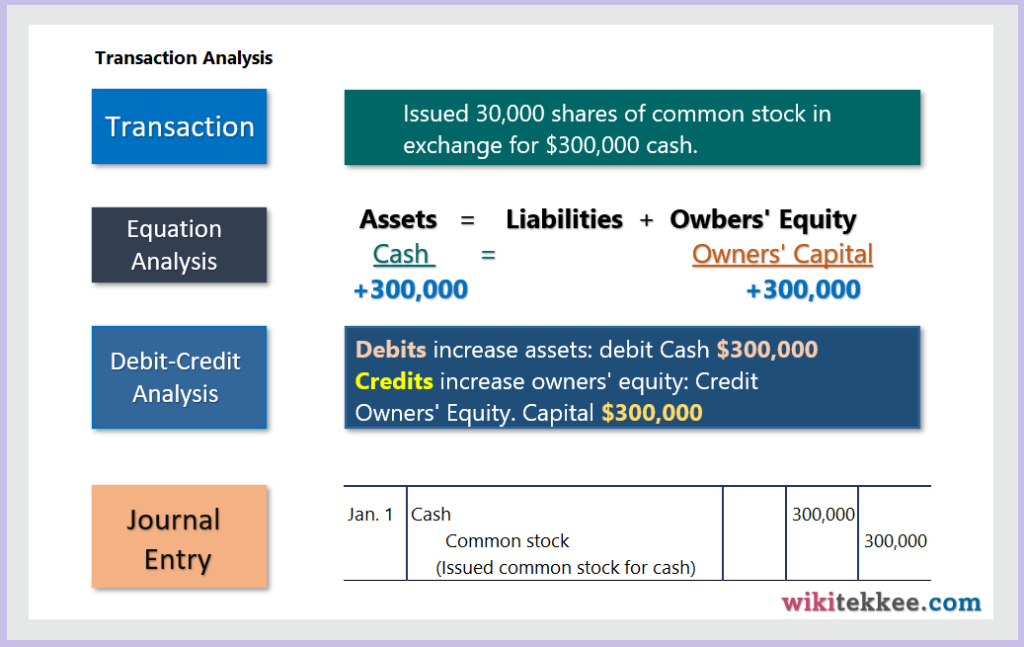
Transaction 1: Issued 30,000 shares of common stock in exchange for $300,000 cash.
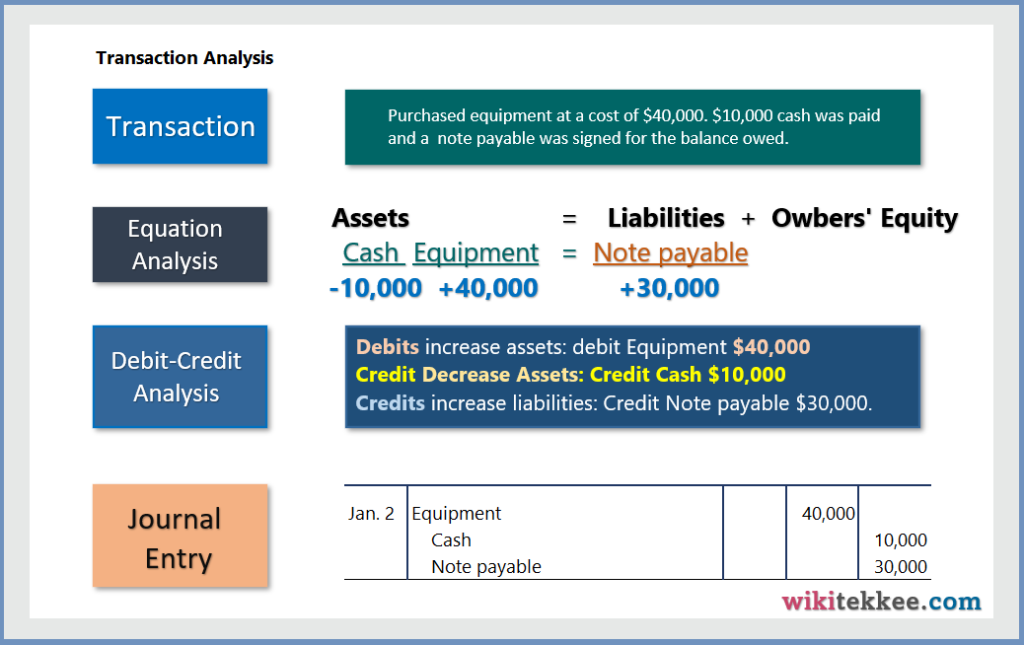
Transaction 2: Purchased equipment at a cost of $40,000. $10,000 cash was paid and a note payable was signed for the balance owed.
3. Preparing Journal Entry:
To prepare journal entries, accountants must know the golden rules of debit-credit. The following image explains the golden rule of debit-credit.
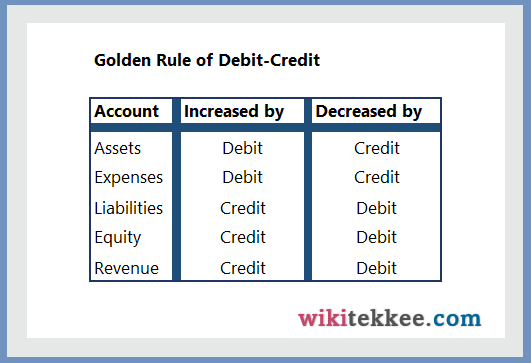
A customized Rule of Debit-Credit:
Let’s extend the accounting equation:
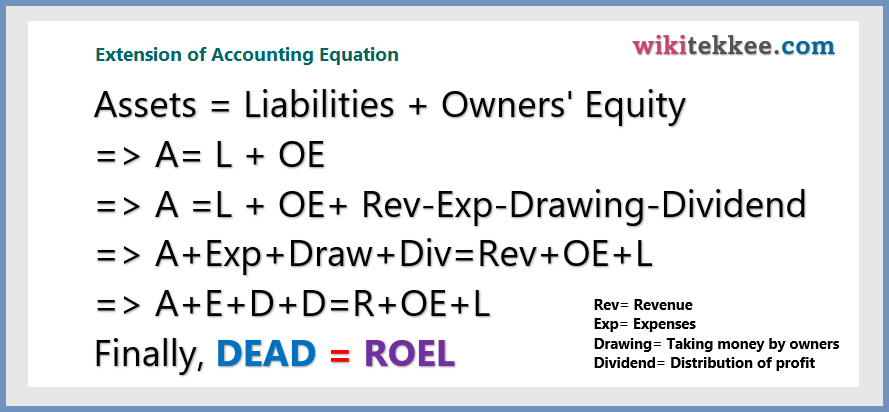
From the above extension, we found that DEAD = ROEL.
Now, you just remember, one sentence to make debit-credit.
DEAD Increase DEBIT
It means, the increase in Drawing, Expenses, Assets, and Dividend will be DEBIT. Therefore, the opposite is ROEL increase CREDIT. It means that increase in Revenue, Owners’ Equity, and Liabilities will be CREDIT.
Example 1: Purchased Rainbow Golf Land for $15,000 cash. The price consists of land
$12,000 and equipment $3,000.
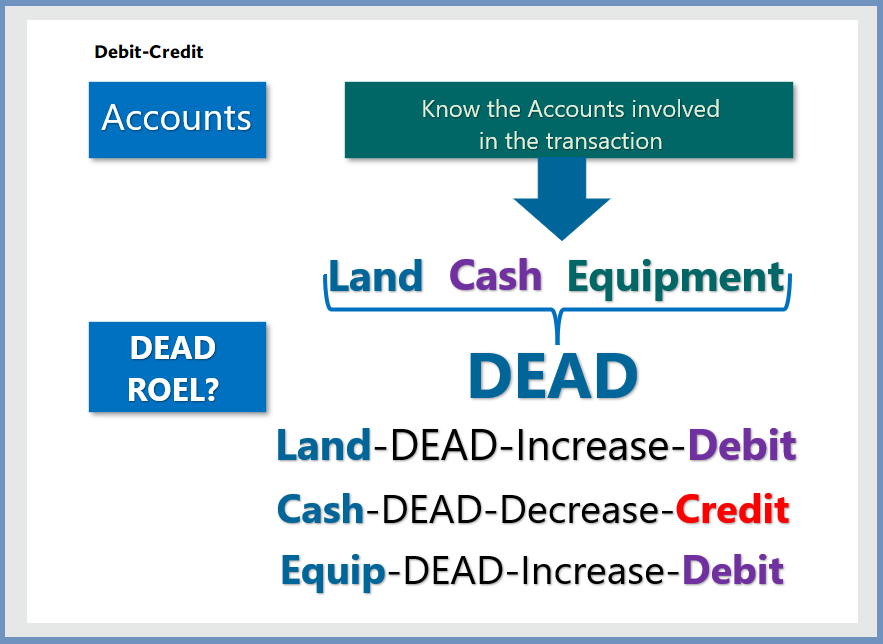
Therefore, the Journal Entry is:

5. Posting to Ledger:
After recording the transactions in the journal, the next step is to post to individual ledger account. Let’s see how to post to ledger.
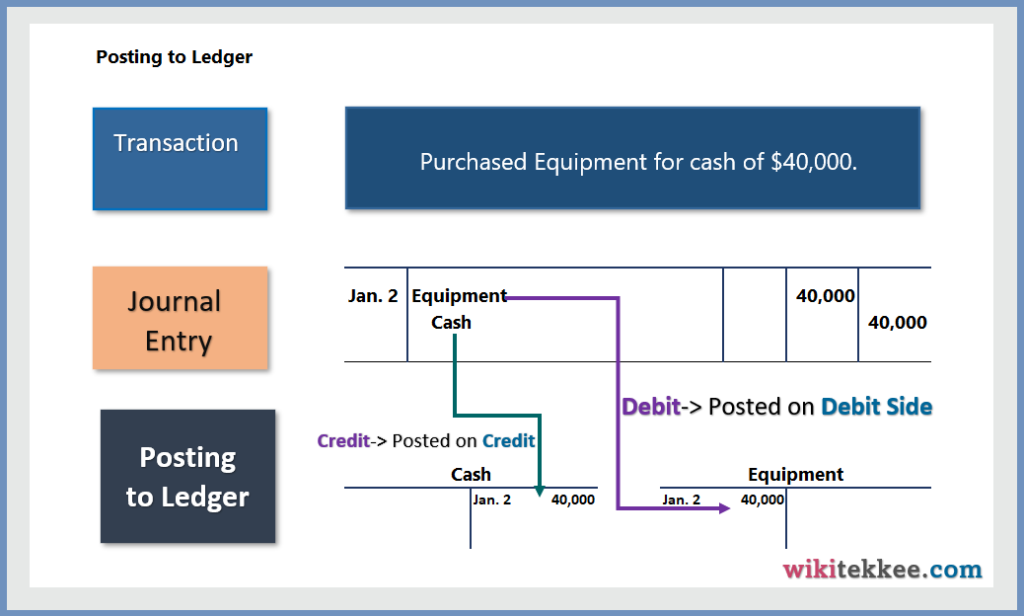
6. Preparing Unadjusted Trial Balance:
After the posting transactions to ledger accounts, the next step is to prepare a trial balance, which is the list of all the accounts with their ending balances. The problem and Excel Template can be downloaded from the following links:
More related readings:



4 Responses