Theoretical structure of financial accounting
The theoretical structure of accounting explains the basic principles of financial accounting. In this section, we discuss the financial accounting, the conceptual framework of financial accounting, cash vs accrual accounting, GAAP, FASB, objectives of financial reporting, qualitative characteristics of financial information such as relevance,
In this section:
- What is Financial Accounting?
- Who are the interested users of financial reporting?
- Cash Vs Accrual Basis of Accounting.
- GAAP, FASB, and IFRS
- Conceptual Framework of Accounting.
- Objective of General-Purpose Financial Reporting
- Qualitative characteristics of Financial Information
- Basic Assumptions
- Accounting Principles

1. What is Financial Accounting?
Financial accounting is the field of accounting concerned with the summary, analysis and reporting of financial transactions relating to a business.
The Financial Accounting consists of three basic activities:
I.Identification [Economic events],
II. Recording [Journal, ledger], and
III.Communication [Preparing income statements etc.]
of the economic events of an entity to interested users.
2. Who are the interested users of Financial Reporting?
The need of financial information depends on the type of users. There are two broad groups of users of financial information:
- Internal users, and
- External users
1. Internal Users:
The internal users of accounting information are managers who plan, organize, and run the business.
They are:
•Marketing Managers
•Production Managers
•Financial Directors, and Company Officers
2. External Users:
The external users of accounting information are individuals and organizations outside a company who want financial information about the company.
Two common external users:
•Investors
•Creditors
Other:
•Analysts
•Government Agencies
•Tax authorities
•Customers, Labor Unions
3. Cash Vs Accrual Basis of Accounting:
Cash-Basis:
Companies record revenue only when they receive cash and record expense when paid in cash.
The difference between cash receipt and cash payment is net operating cash flows.
Example:
Ryan company paid $60,000 for 3 years’ rent at the beginning of Year 1. Under the cash-basis accounting, the rent payment is shown when paid:
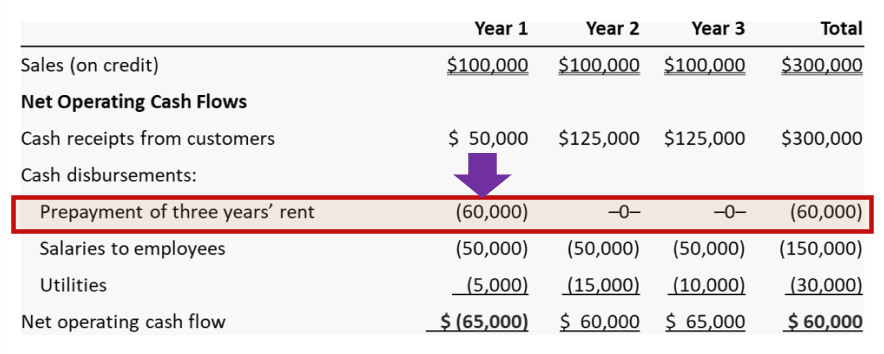
Accrual-Basis:
Companies record revenue when they complete the service performance or the delivery goods. They recognize expenses when incurred irrespective of cash payment.
Example:
Ryan company paid $60,000 for 3 years’ rent at the beginning of year 1. Under accrual-basis accounting, rent is recognized as an expense all three years even when it was paid in year 1.
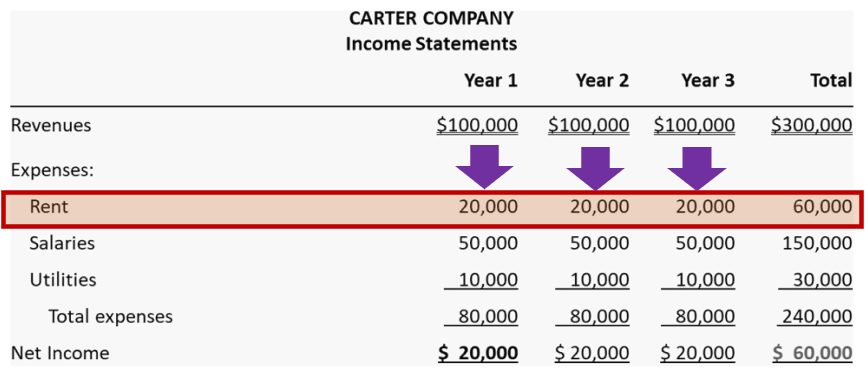
4. GAAP, FASB, and IFRS:
The accounting profession has developed standards that are generally accepted and universally practiced. This common set of standards are called Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
The primary accounting standard setting body in the United States is the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is the agency of the U.S. government that oversees U.S. financial markets and accounting standard setting bodies.
Countries outside the U.S. have adopted International Accounting Standards (IAS). These standards are called International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
5. Conceptual Framework of Accounting:

•Described as an Accounting Constitution.
•The Conceptual Framework sets out the fundamental concepts for financial reporting that guide the Board in developing IFRS Standards. It helps to ensure that the Standards are conceptually consistent and that similar transactions are treated the same way, so as to provide useful information for investors, lenders and other creditors.
•The Conceptual Framework also assists companies in developing accounting policies when no IFRS Standard applies to a particular transaction, and more broadly, helps stakeholders to understand and interpret the Standards.
History of Conceptual Framework of Accounting:

1989 Vs 2018:
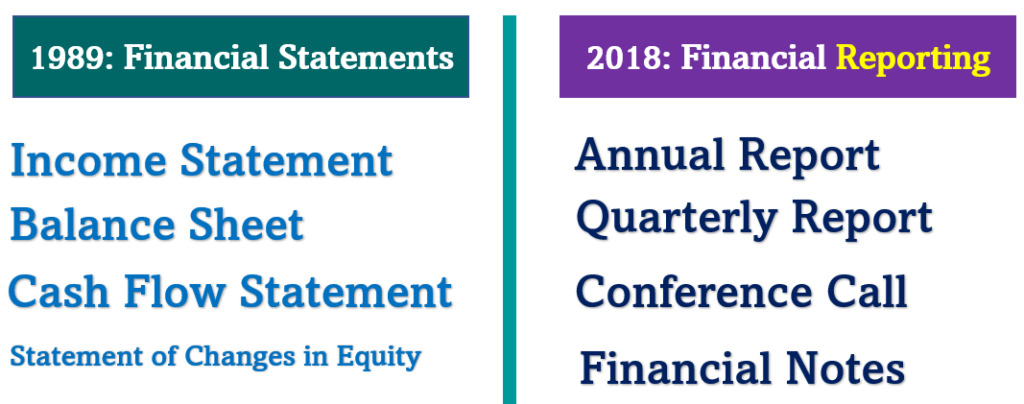
6. Objective of General-Purpose Financial Reporting:
•To provide information about a reporting entity’s economic resources, claims to those resources, and changes in resources and claims.
•A= L+ OE
•To provide financial information about companies that is useful to capital providers in making decisions.
_____Investors decide whether to buy, sell, and hold equity or debt securities.
_____Creditors decide whether to provide or settle loans.
•To provide information that is useful to capital providers.
•To help identify strength and weaknesses and assess liquidity and solvency of company.

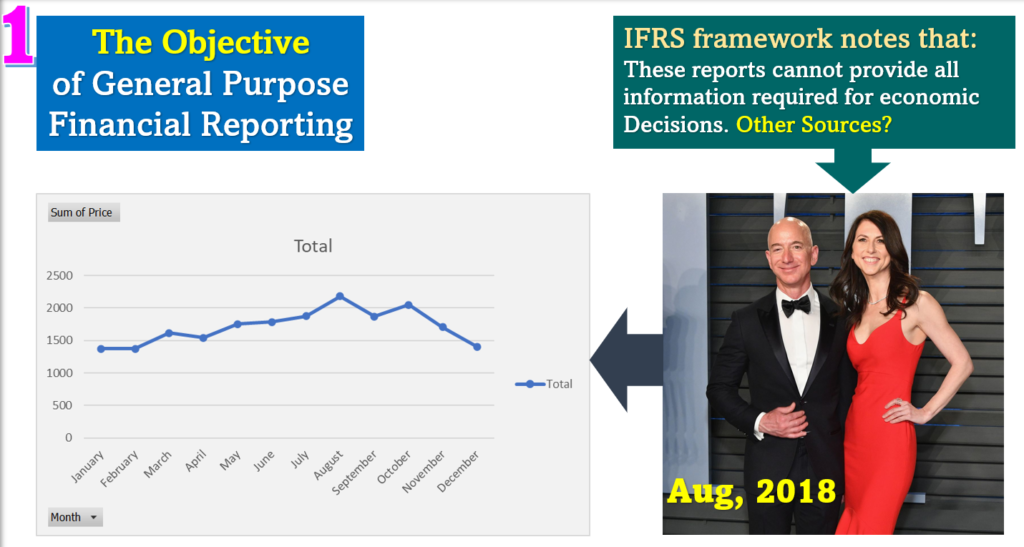
What are the other sources: Think about non-financial information that may affect the investors’ sentiment. The announcement of Jeff Bezos and his wife was published on news media sometimes in August, 2018, and the investors were uncertain about the Amazon’s future. This uncertainty led to the decline of the stock price. See the image below for better understanding.
7. Qualitative characteristics of Financial Information:
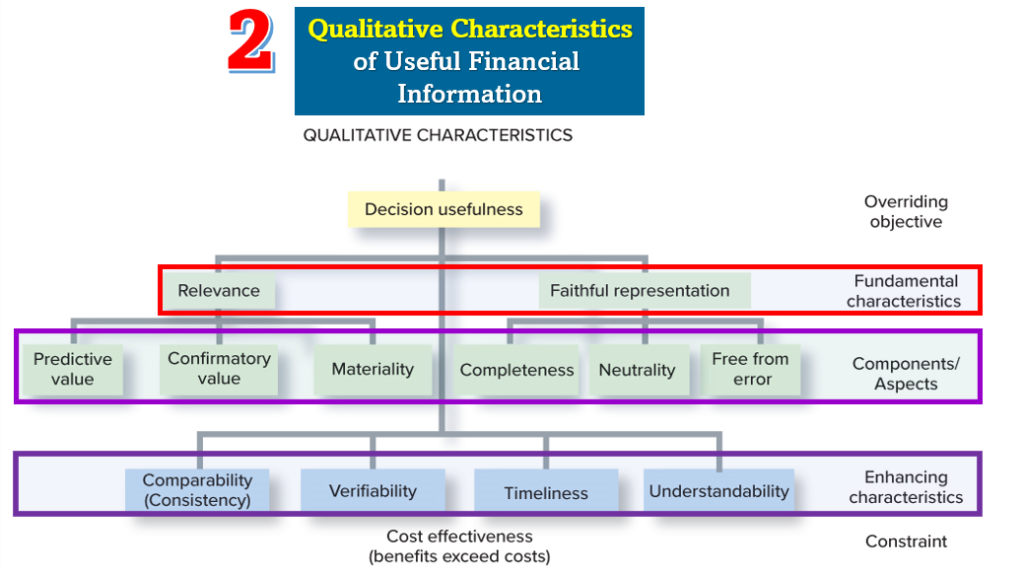
The decision usefulness of information depends on the quality of information. Note that these characteristics are intended to enhance the decision-usefulness of information.
1. Fundamental Qualitative Characteristics:
•For financial information to be useful, it should possess the fundamental decision-specific qualities of:
_____Relevance
_____Faithful representation
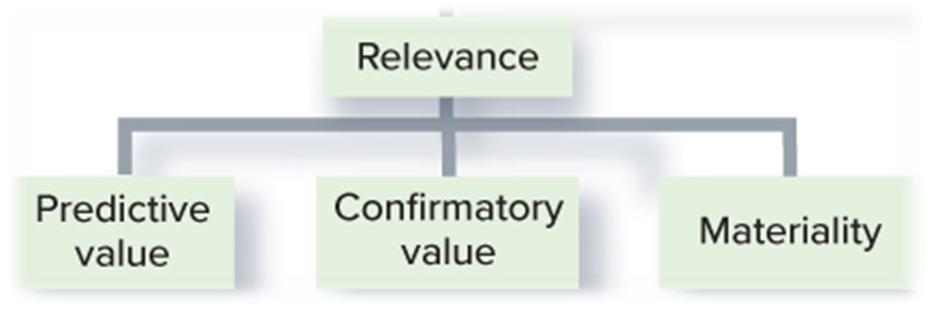
•To be relevant, information must make a difference in the decision process. To be relevant, information MUST have :
•____Predictive value: Helps users predict a company’s future cash flows.
•____Confirmatory value: Helps investors confirm or change their prior assessment regarding a company’s cash-flow generating ability.
•____Materiality: Information is material if it has an effect on decision.
Predictive value and Confirmatory value example:
Faithful Representation:
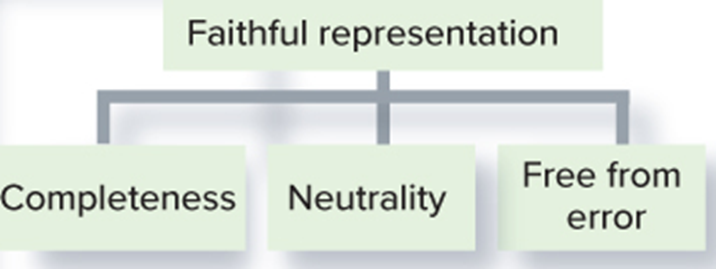
•Faithful representation exists when there is an agreement between a measure or description and the phenomenon it purports to represent. Faithful representation requires that information be
•____Complete: Includes all the information necessary.
•____Neutral: Information is free from bias.
•____Free from error: Information contains no error or omission.
Enhancing Qualitative Characteristics:
•Comparability: Accounting information capable of being compared with information from other companies in the same period. To be comparable, all companies in the same industry MUST follow the same accounting methods.
•Verifiability: Information capable of being checked for accuracy, completeness, and reliability.
•Timeliness: Information made available to users early enough to help them make decisions.
•Understandability: Information sufficiently transparent so that it makes sense to reasonably informed users of the information.
Elements of Financial Statements:
SFAC 6 defines 10 elements of financial statements. These elements are “the building blocks” with which financial statements are constructed—the classes of items that financial statements comprise:
The 10 elements are: (1) assets, (2) liabilities, (3) equity, (4) investments by owners, (5) distributions to owners, (6) revenues, (7) expenses, (8) gains, (9) losses, and (10) comprehensive income.
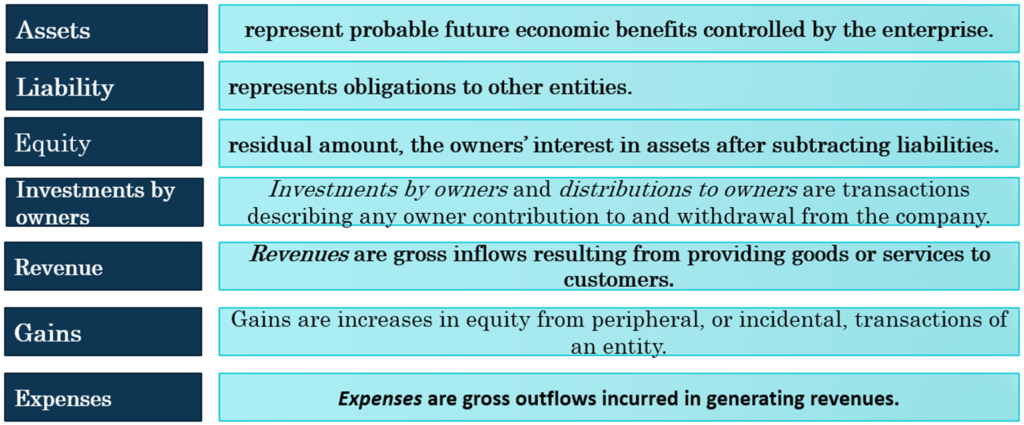
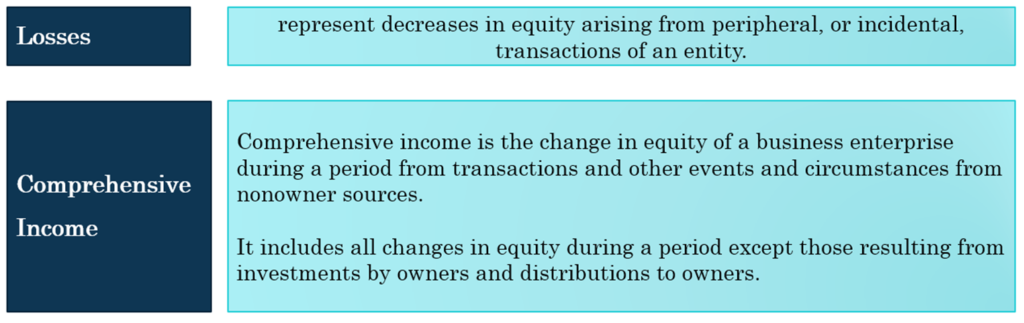
8. Basic Assumptions:
Four basic assumptions underlie GAAP:
•The economic entity assumption presumes that economic events can be identified specifically with an economic entity. The ownership and business are separate from each other.
•The going concern assumption anticipates that a business entity will continue to operate indefinitely.
•The periodicity assumption allows the life of a company to be divided into artificial time periods to provide timely information.
•The monetary unit used in U.S. financial statements is the U.S. dollar.
9. Accounting Principles:
•The historical cost principle states that asset and liability measurements should be based on the amount given or received in the exchange transaction.
•Realization Principle: Revenue should be recognized when the earnings process is virtually complete, and collection is reasonably assured. Revenue is recognized when earned, regardless of when cash actually is received.
•Matching Principle: Expenses are recognized in the same reporting period as the related revenues
•Full Disclosure: Any information useful to decision makers should be provided in the financial statements, subject to the cost effectiveness constraint.
More related readings:

One Response